Modern world history, the modern era, or the modern period is the global, linear, historical-geographical approach to the time frame that comes post-classical history. Perhaps, this view is in contrast to the non-linear or rather the organic view of history which was initially put forth by the famous historian and philosopher Oswald Spengler in the early 20th century.
Division of Modern History
We can divide modern history into three main periods i.e. the early modern period, the late modern period, and the contemporary history.
Early Modern Period
The early modern period began approximately at the beginning of the 13th century. In this period, the major historical milestones include the Expansion and contraction of major European and Asian civilizations, the Age of Discovery, the European Renaissance as well as the Protestant Reformation.
Late Modern Period
On the other hand, the late modern period started in the mid of 18th century. The American Revolution, the French Revolution, the Great Divergence, the Industrial Revolution, and the Russian Revolution happened in this period. Primarily, it took most of human history up to the year 1804 for the population of the modern world to reach its 1 billion mark. However, the next billion came just over a century later in the year 1927.
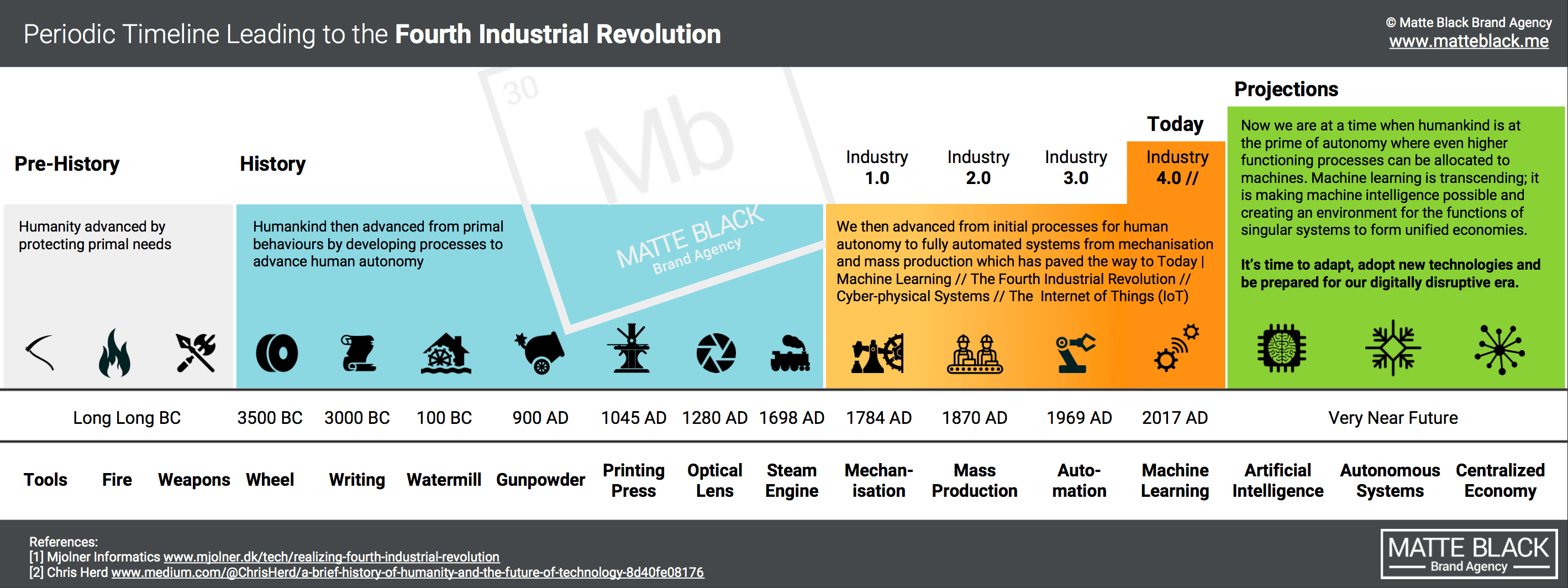
Contemporary History
Contemporary history includes the span of historical events starting from 1945. These events are most relevant to the present time and scenario. Many historians describe the early modern period as the time frame between 1500 and 1800. This period mainly follows the Late Middle Ages period. Further, it is marked by the initial European colonies, the beginnings of recognizable nation-states as well as the rise of strong centralized governments.
Impact on the Modern World
In the Ottoman Empire and Africa, the Muslim expansion took place in East and North Africa. However, in West Africa, several native nations existed. The civilizations of Southeast Asia and the Indian Empires played a pivotal role in the spice trade. In the Indian subcontinent, the presence of the Great Mughal Empire was strong. Moreover, the archipelagic empires, the Sultanate of Malacca and later the Sultanate of Johor, exercised power over the southern areas.
In the Asian subcontinent, different Japanese shogunates and the Chinese dynasties held power. The Edo period from 1600 to 1868 in Japan is regarded as the early modern period. On the other hand, in Korea, the period from the rising of the Joseon Dynasty to the enthronement of King Gojong is referred to as the early modern period.
In the Americas, Native Americans started a huge and distinct civilization which included the Aztec Empire and alliance, the Inca civilization, the Mayan Empire and cities, and the Chibcha Confederation. However, in the west, the European kingdoms and movements were in a movement of reformation and expansion. Russia made its way to the Pacific coast in 1647. It went on to consolidate control over the Russian Far East in the 19th century.
More About Modern World History
The religious trends of this period witnessed the rise of the Muslim community and the Muslim world. Christians and Christendom saw the end of the Crusades. Religious Unity under the Roman Church came to an end. Moreover, in this period, the Inquisitions and Protestant reformations also took place.
Also during the early modern period, people witnessed the age of discovery and trade. This happened as a result of the collective effort of the Western European nations. Portugal, Spain, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and France went on a colonial expansion. These nations took possession of lands and set up colonies in Africa, southern Asia, and North and South America. Turkey went on to colonize Southeastern Europe, as well as parts of West Asia and North Africa. Russia, on the other hand, took possession in Eastern Europe, Asia, and North America.
